[课程笔记]UCB CS61B
Java 数据结构课程,因为懒所以荒废了很久。。
讲课十分有趣清晰,老师很逗( •̀ ω •́ )✧
1.2 Defining and Using Class
javac: compile the java file to class file
java : run the compiled program

why make a class file?
- type check
- ‘simpler’ to execute, distributed code is faster
- protects your intellectual, NO need to give out source code
for every single dog make a new class ?
classe can contain not just functions, but also data
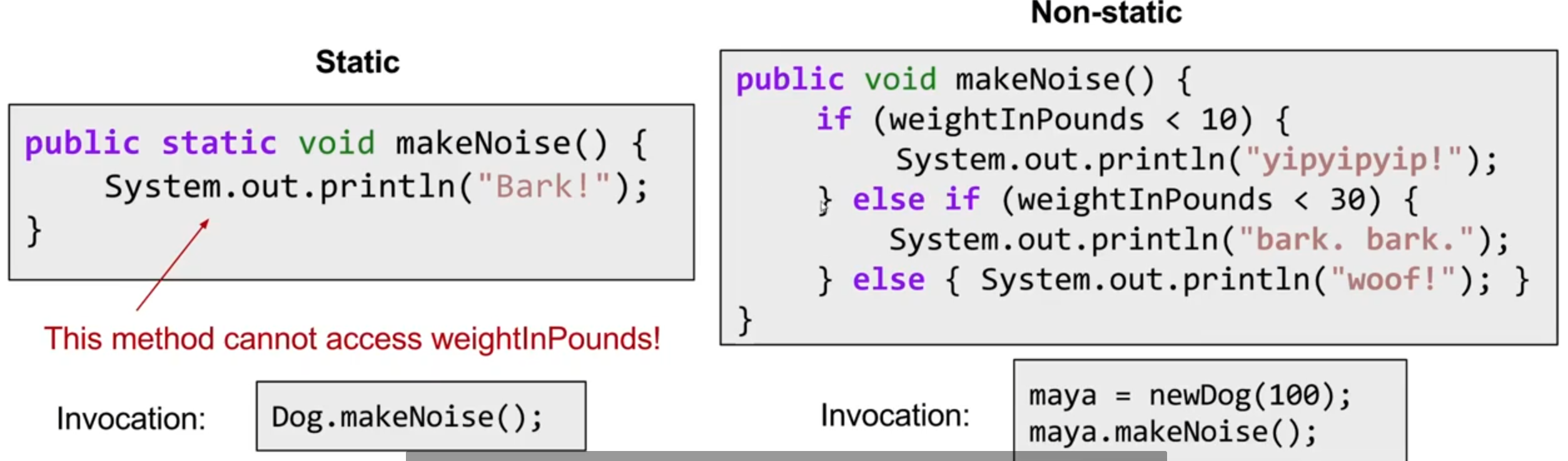
static method and instant method
 some classes never instantiated like **math** class
some classes never instantiated like **math** class
 i = 0 bark
i = 1 woof
i = 2 woof
i = 3 ? not initialized
i = 0 bark
i = 1 woof
i = 2 woof
i = 3 ? not initialized
i=3 is not a dog at all
public static void main(String[] args)
command ling argument
Exercise

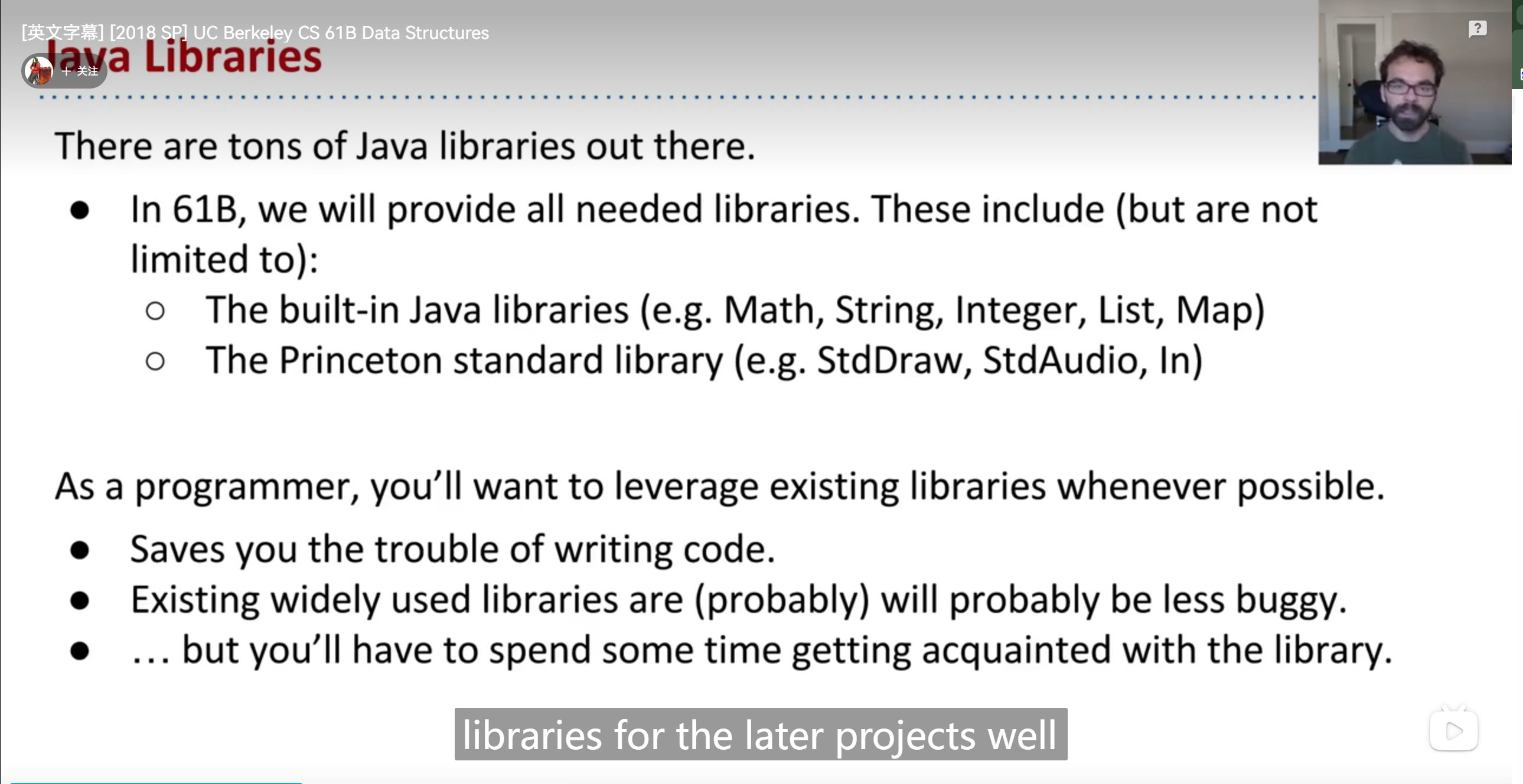
using libraries
amazing and cool thing of being a programmer
2.1References Recursion and Lists

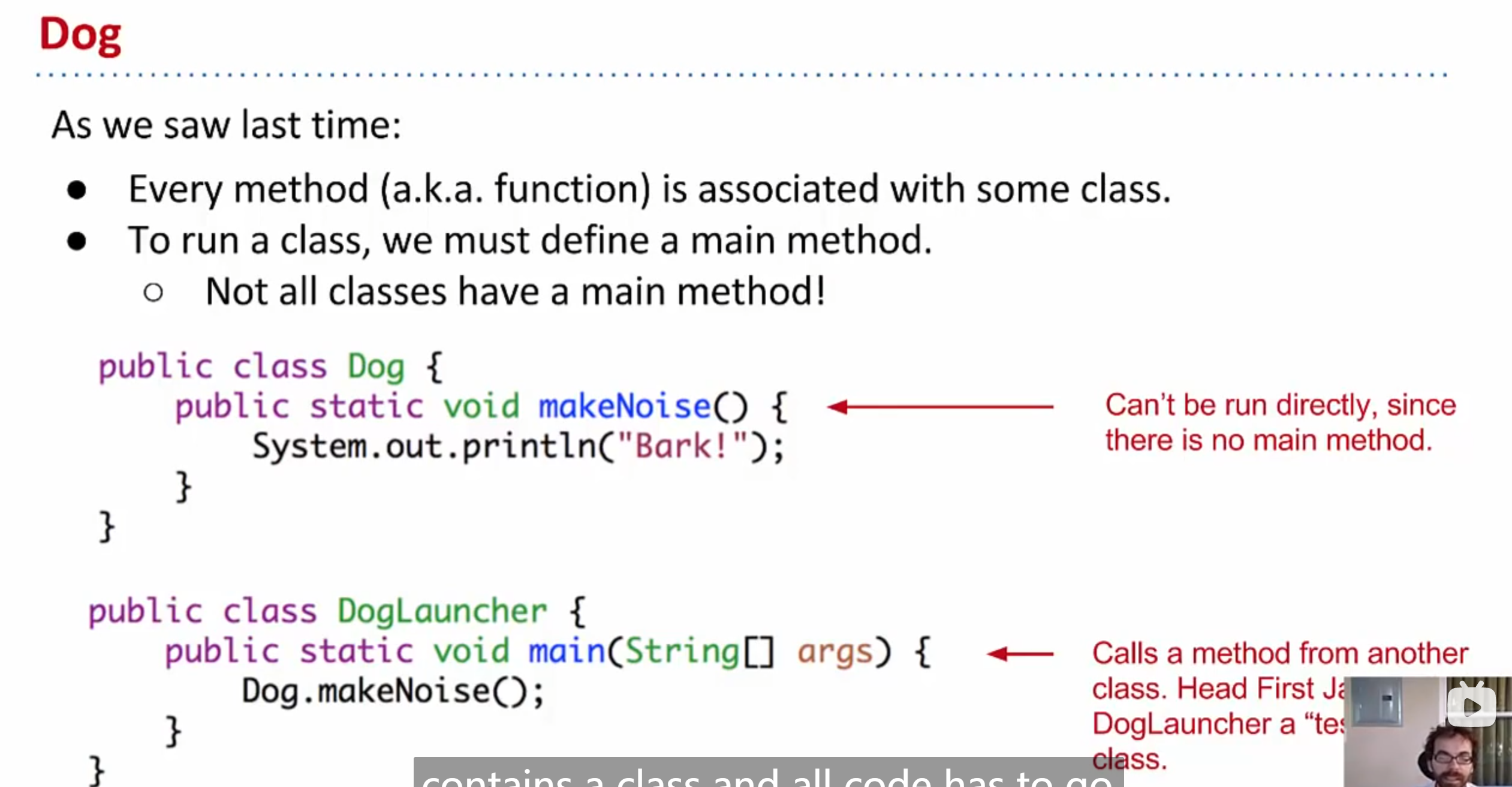
In class Dog
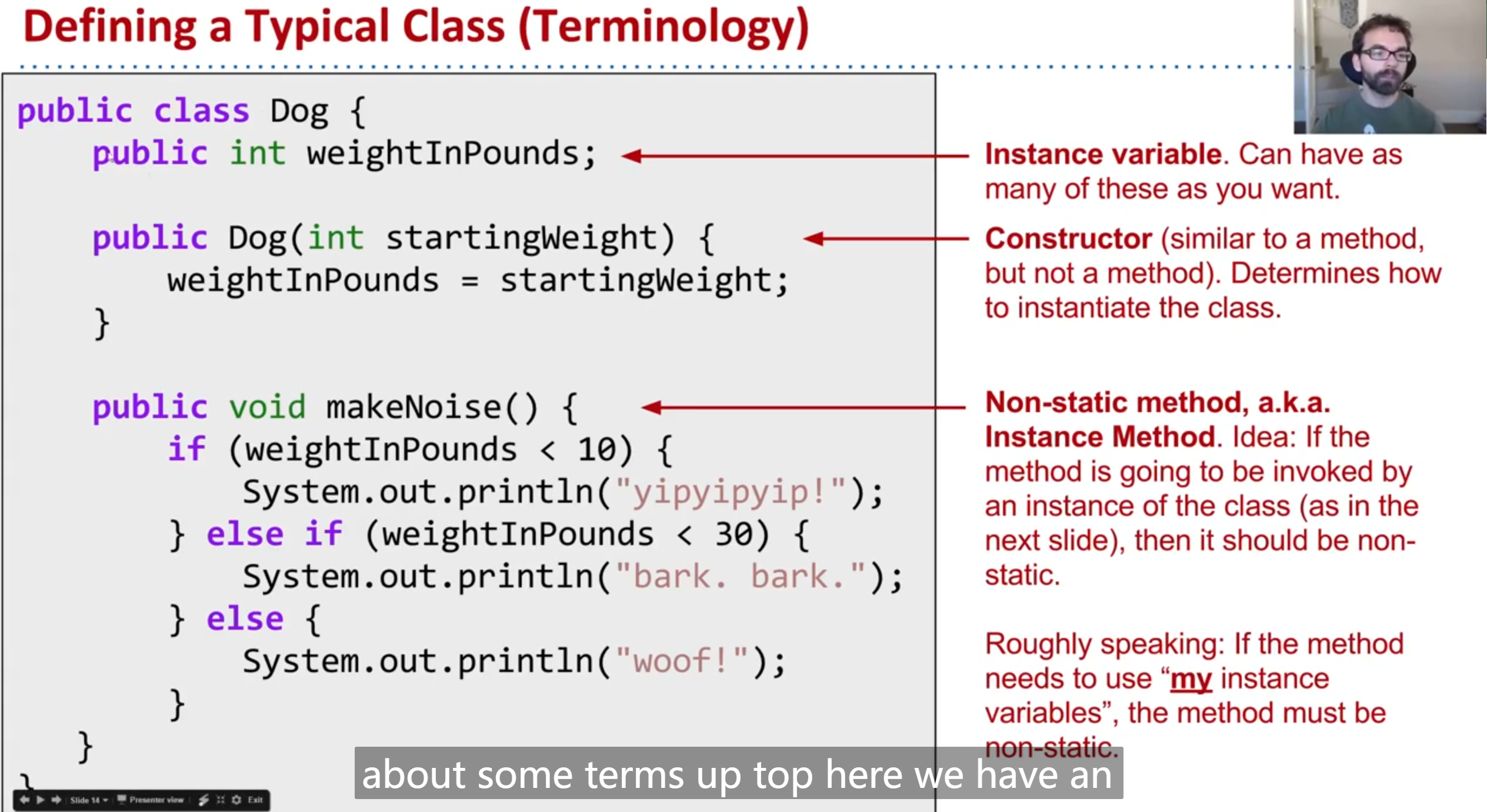
many instance variables
static variables every dog shares this variable
constructor determine how to instantiate the class Dog in launcher , looks like a method(but its not)
instance method : the method is going to be invoked by a instance variable in this class, then it should be instance(non-static)

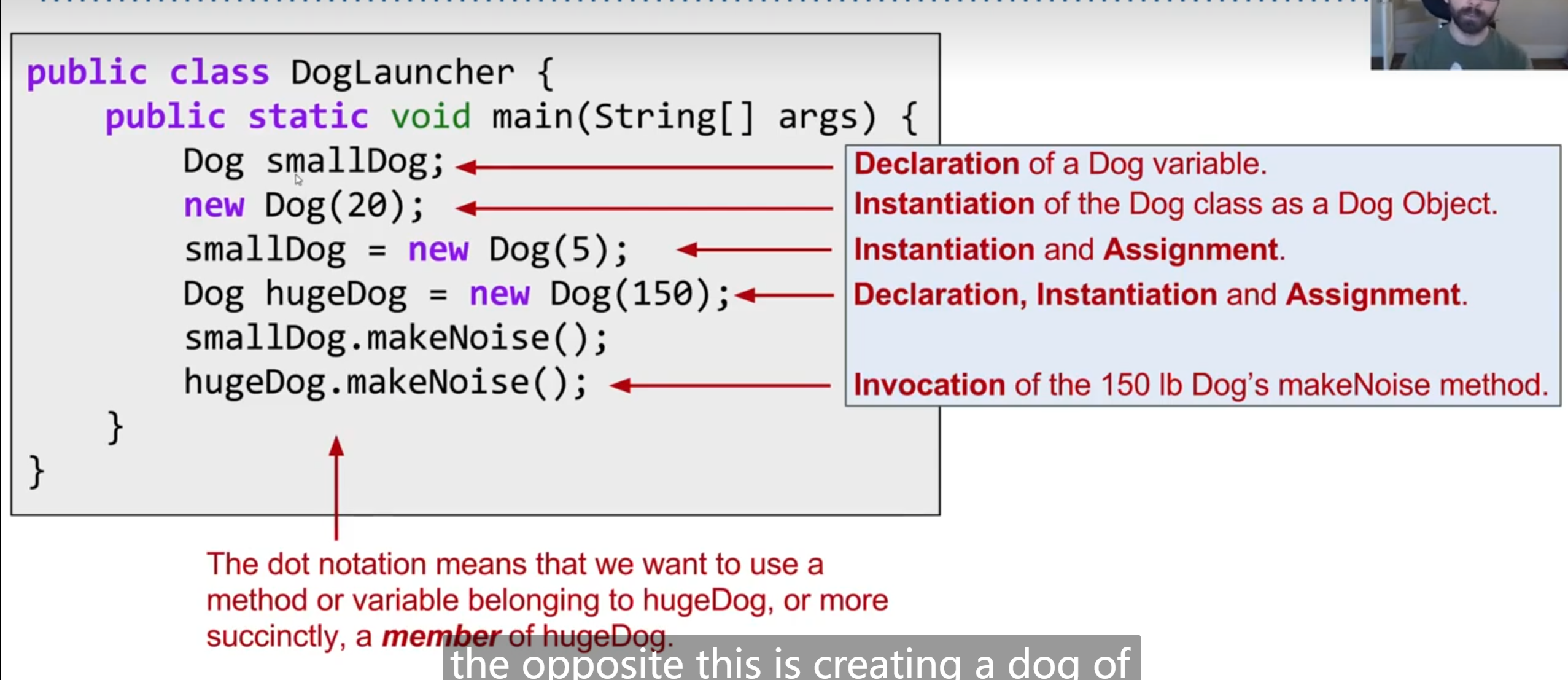
In LaunchDog
declaration : declares a variable belongs to a specific class
instantiation : create a new dog
assignment : assign the new dog to a variable
Variables in Java
 ~~NO?~~
YES
~~NO?~~
YES
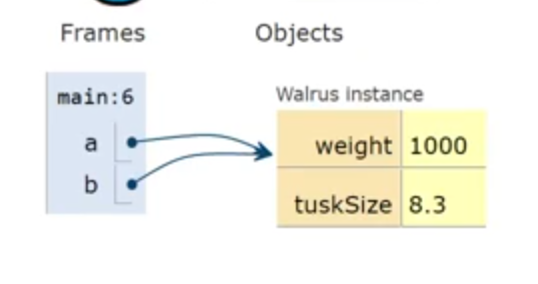
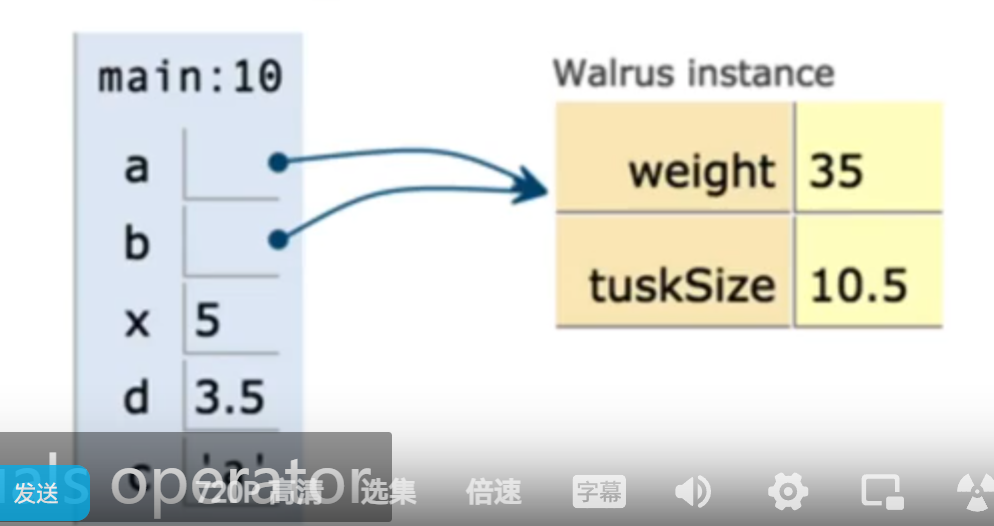
a and b are like pointers
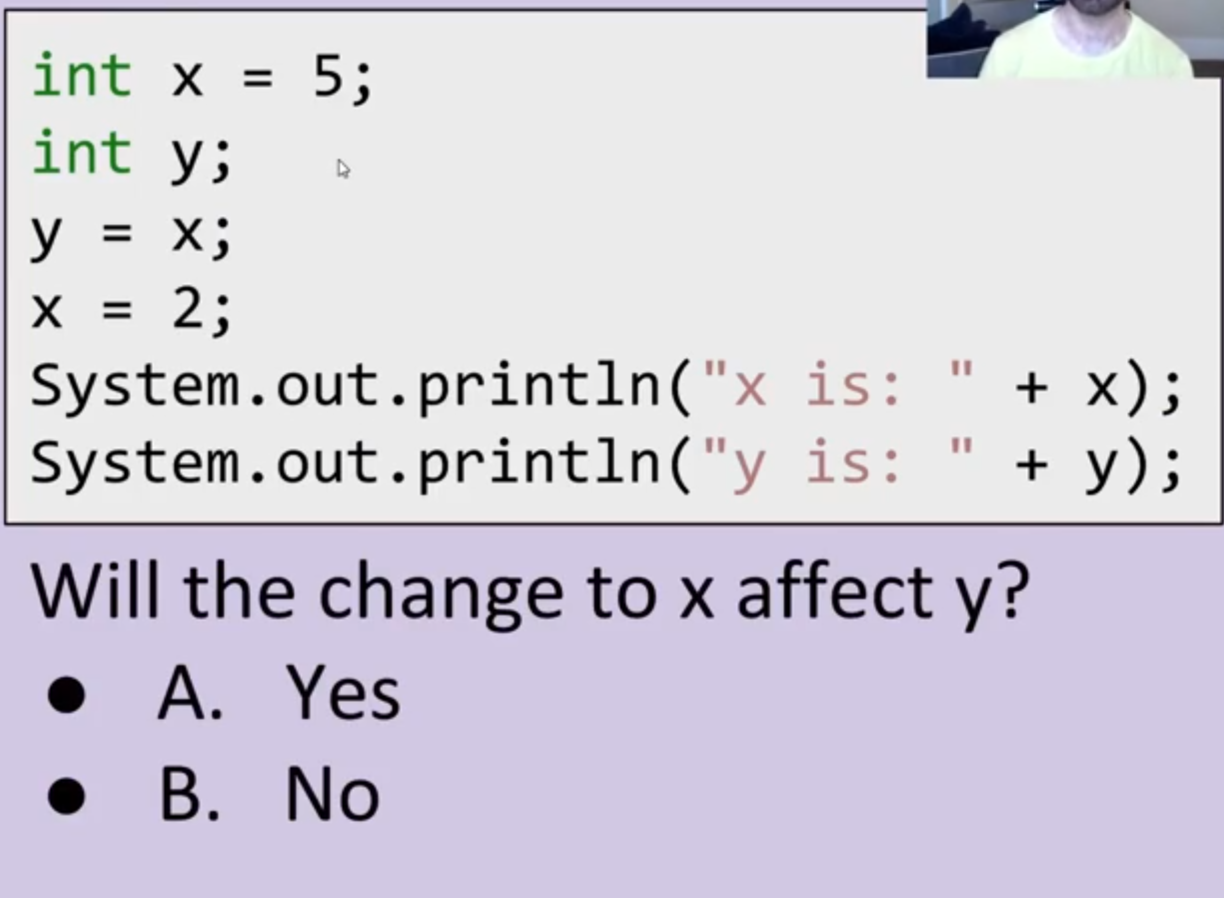 NO? NO!
NO? NO!
 simply changing the values
y copies x
simply changing the values
y copies x
types
tells how to interpret these bits in the memory
- byte
- short
- int
- long
- float
- double
- boolean
- char
declaration and assignment
get boxes and filled up with certain bits
Reference type
class instantiation
 **new** : find bits(size of the types in the class)
"return" the address
**new** : find bits(size of the types in the class)
"return" the address
Declaration of reference type
(a pointer :64bits)
reference type works like an arrow
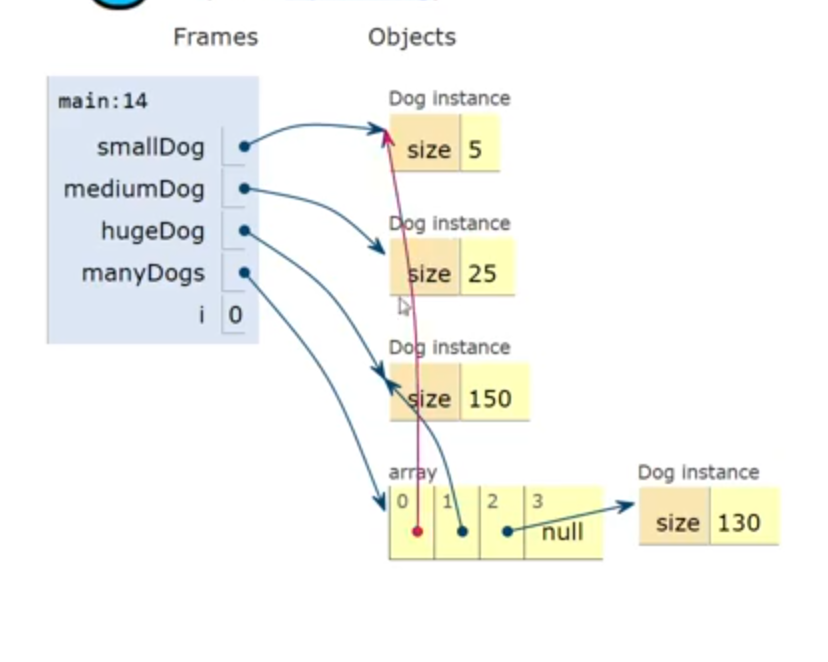
List
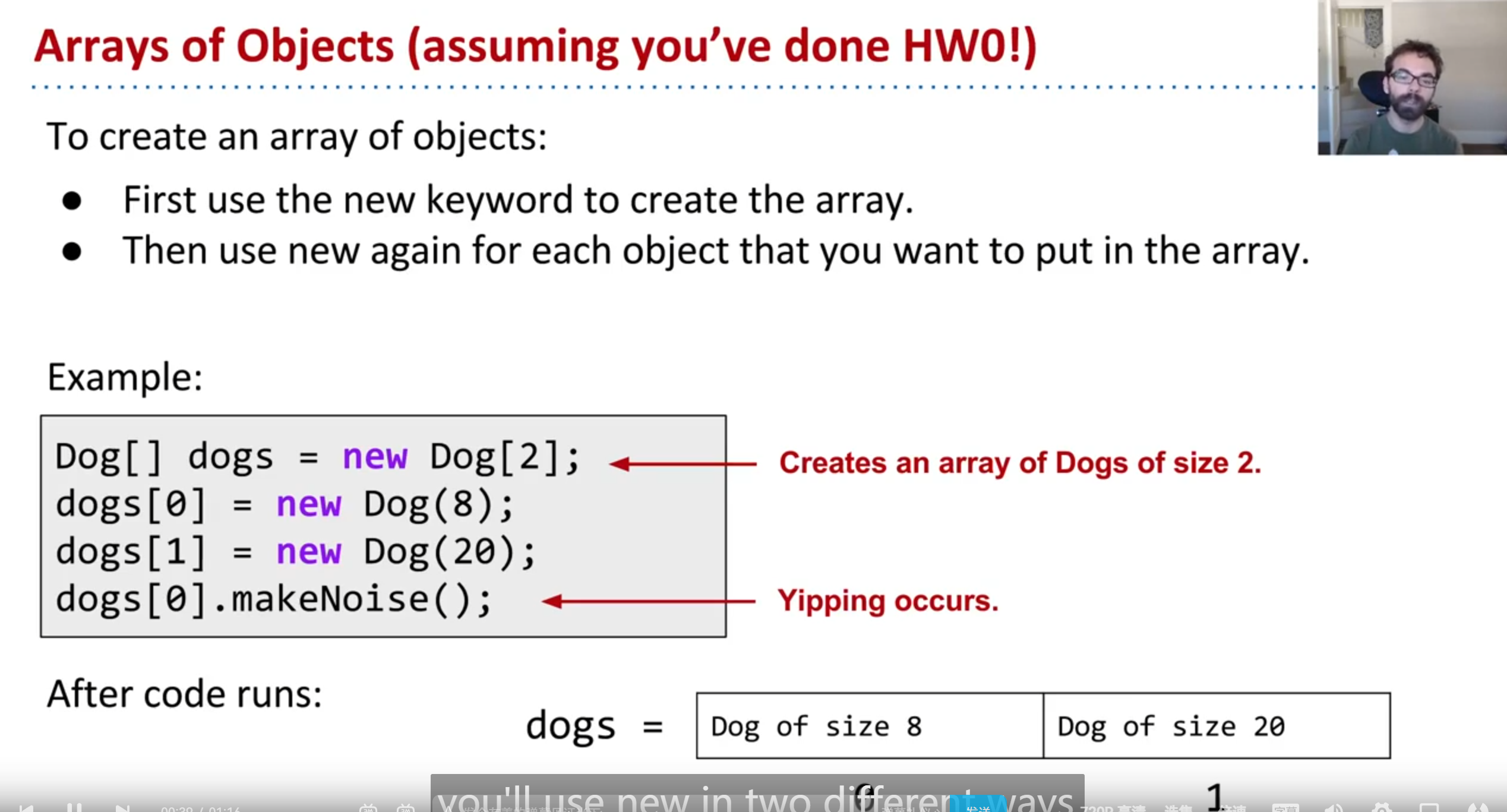
1 | Dog[] dogs = new Dog[2] //create 2 dog houses |
Parameter Passing


Declaration and Instantiation of Arrays
1 | Planet p = new APlanet(0,0,0); |
1 | int[] a //Declaration (create a new box, no object is insrantiated) |
Int List
1 | public class IntList { |

1 | public class IntList { |
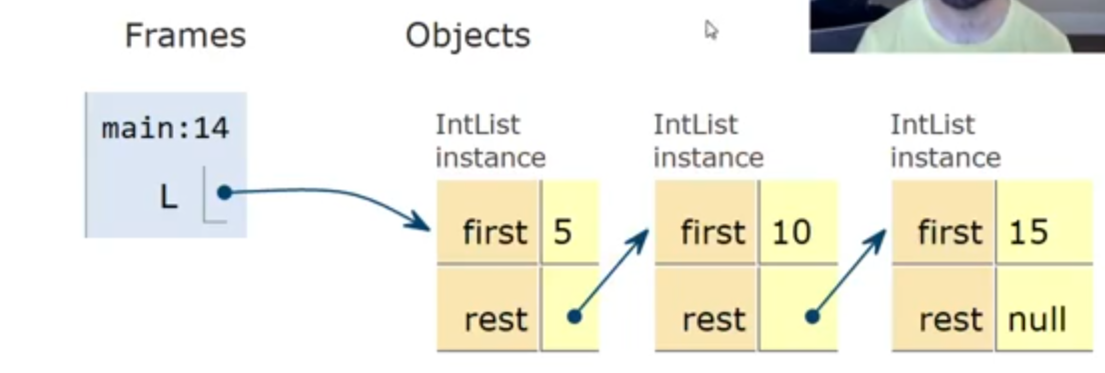
add methods
1.size
1 | public int size() { |
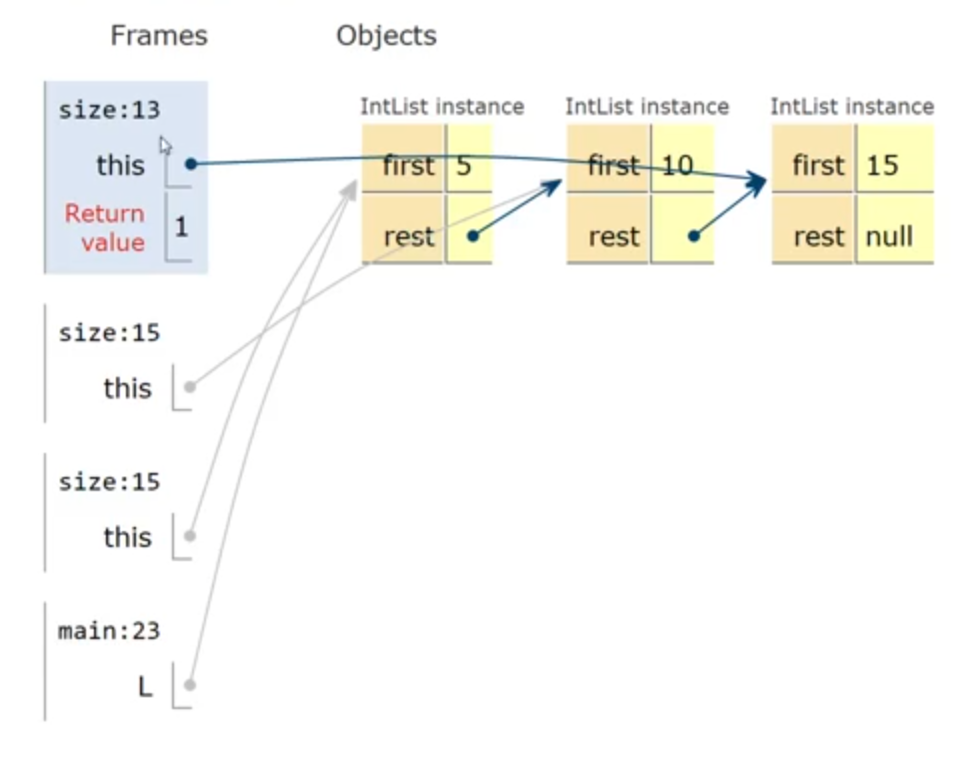
1 | //return the size without using recursion |
2.get
1 | public int iterativeGet(int i) { |
become a super magical list creator





![[CTF实战]QQ盗号网站SQL注入攻击](https://s2.loli.net/2024/07/15/kdInMjAyZSuUBb7.png)
![[misc]网站搭建中使用的python脚本和HTML前端代码](https://s2.loli.net/2024/07/15/eM2UuLr5t37XmF9.png)
![[CS学习]计算机网络](https://s2.loli.net/2024/07/15/3gzkTo129CQZXKP.png)
![[CTF技术]SQL注入攻击](https://s2.loli.net/2024/07/14/AJYsj9Mu2VKmHnz.png)